
Table of Contents
- 15 Advanced Google Search Tips and Tricks
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Google, the most robust search engine on the planet, has revolutionized the way we find information. It holds a little over 92% of the global search engine market share. Therefore, it wouldn’t be wrong to say that Google has become an indisputable reality of life in terms of how we find and receive information. We use it to find where we’re going, what we should eat, what’s in theaters; but most significantly, it’s our primary source of learning and accomplishing crucial tasks.
But, unless you’re a techie, you’re probably still using Google in the most basic way. Therefore, if your current Google experience consists of typing a few words and modifying your query until you discover what you’re looking for, we’re here to inform you that there’s a better method—and it’s not difficult to learn. However, even if you are a technology whiz who already knows how to search on Google like a pro, we recommend bookmarking this post.

15 Advanced Google Search Tips and Tricks
There are a plethora of Google search commands, tips, and tricks to choose from, but to save you time, we’ve compiled a list of the 15 Google search tips that are the most useful. These Google search techniques will make your job easier, faster, and more effective, and will allow you to use Google search to its full potential.
1. Quotation marks
When searching for a certain term, one of the simplest and most effective search techniques is to utilize inverted commas. The quotation marks instruct Google to look for the entire phrase rather than individual words. Therefore, when looking for something specific, try using quotes to avoid surfing through irrelevant results, and save your time.
Let’s understand this with an example. Let’s assume you’re looking for content marketing information on Google. Rather than merely typing content marketing into the Google search box, you should search for the specific keyword. To do this, simply double-quote the search query.
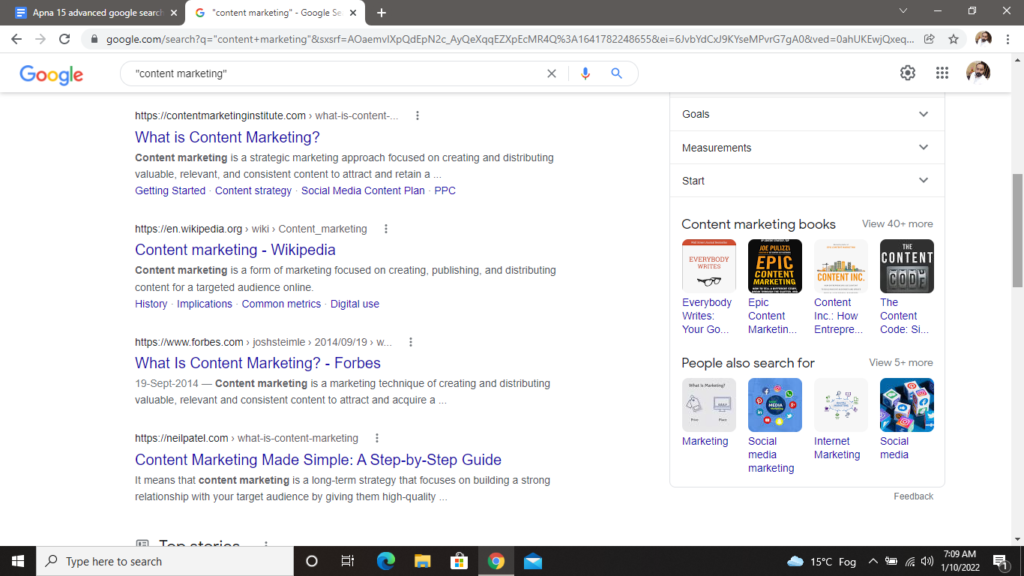
Moreover, using inverted commas is a wonderful method to find highly particular information, such as a famous quote, a person, or even a specific product.
2. Conversions
When performing conversions such as metric conversions, currency conversions, etc., directly type the units in the search box, as Google already has all of those conversions built in. For example, if you want to know the value of the American dollar in Indian rupees, simply type “USD to INR”.
3. Calculator
You can even perform calculations in the Google search bar. The commands that you need to use for this include addition, subtraction, multiplication signs, and so on. In the search bar, Google makes the calculation for you naturally, but if you press enter, it activates the Google scientific calculator for a more detailed calculation.
4. Asterisk
One of the most useful commands on the list is the asterisk. When you include an asterisk in a Google search query, it creates a placeholder that the search engine may complete automatically afterwards. If you don’t know all the words to a song, this is a fantastic way to find them.
Let’s understand this with an example: If you search, “Come * right now * me”, Google will look for that phrase, knowing that the asterisks may be any word. So, more often than not, what you’ll find are the lyrics to the song Come Together by The Beatles.
5. “site:” command
It’s possible that you’ll need to use Google to search for content on a particular website. The “site:” command helps you do so. This command restricts the search results to a single domain. The syntax is straightforward. For example, if you search our site by typing “site:peppercontent.io”, you can see all the pages from this domain that have been indexed by Google.
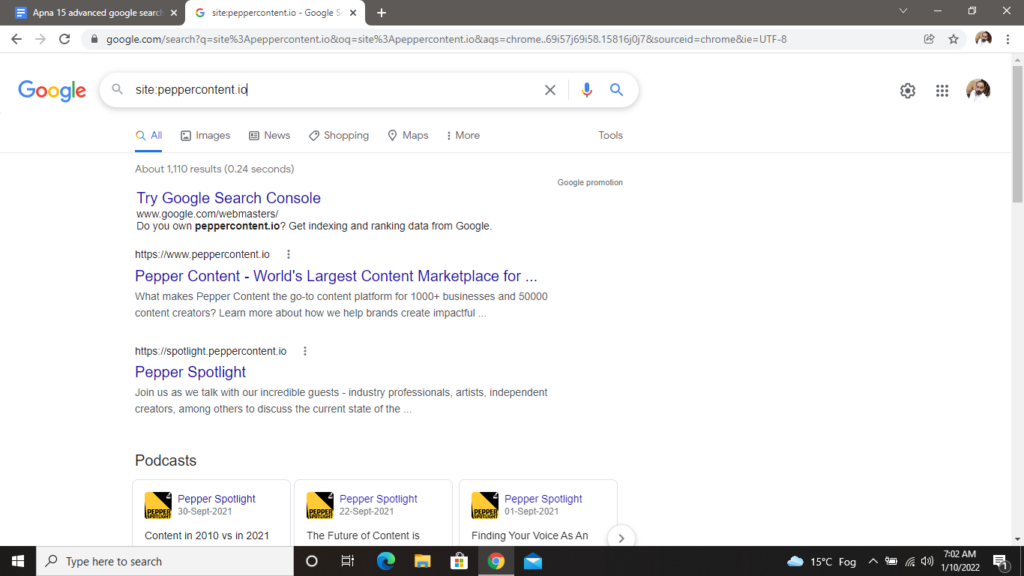
You can also narrow down the results to a specified topic within this domain. For example: “content creation site:peppercontent.io”.
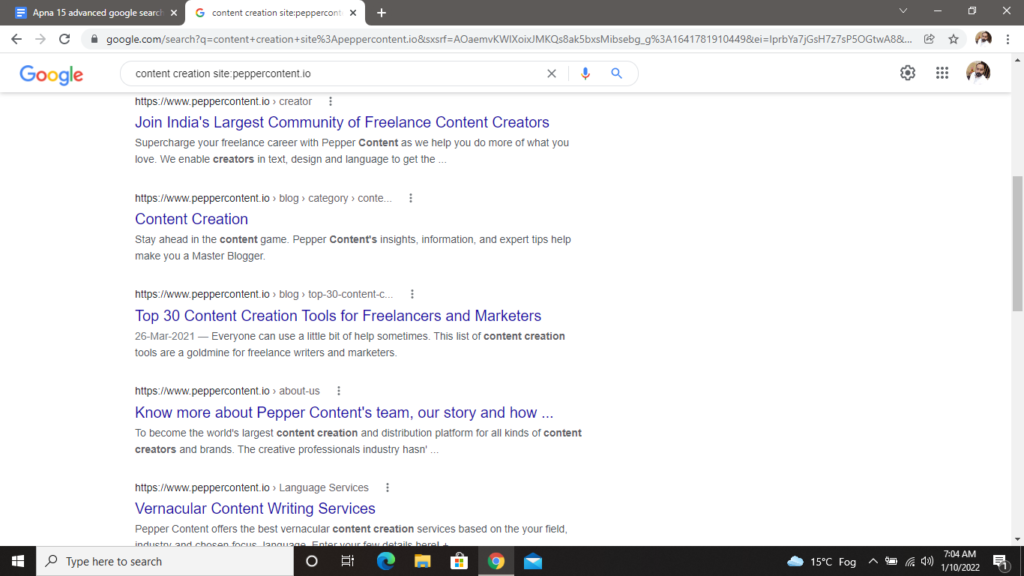
Quick tip: to find information from educational sites, use the term “edu”.
Along with finding indexed pages, you can use this command for competitive analysis, such as determining the number of pages on a given topic your competitor’s site contains. This will assist you in determining how much effort is required to rank for a particular keyword. This command can also be used to verify all the pages on your site that are related to a given topic.
Another great use of this command is to determine which pages on your website are not indexed or whether any pages have been indexed numerous times, resulting in content duplication. This is important, because if your site has 1,500 pages but only 500 of them have been indexed by Google, you would know that something is wrong and needs to be addressed. When searching for indexed pages, you can further narrow down the search to specific categories. For instance, if you search “site.peppercontent.io/blog”, you will get all the blog posts on our site, indexed by Google.
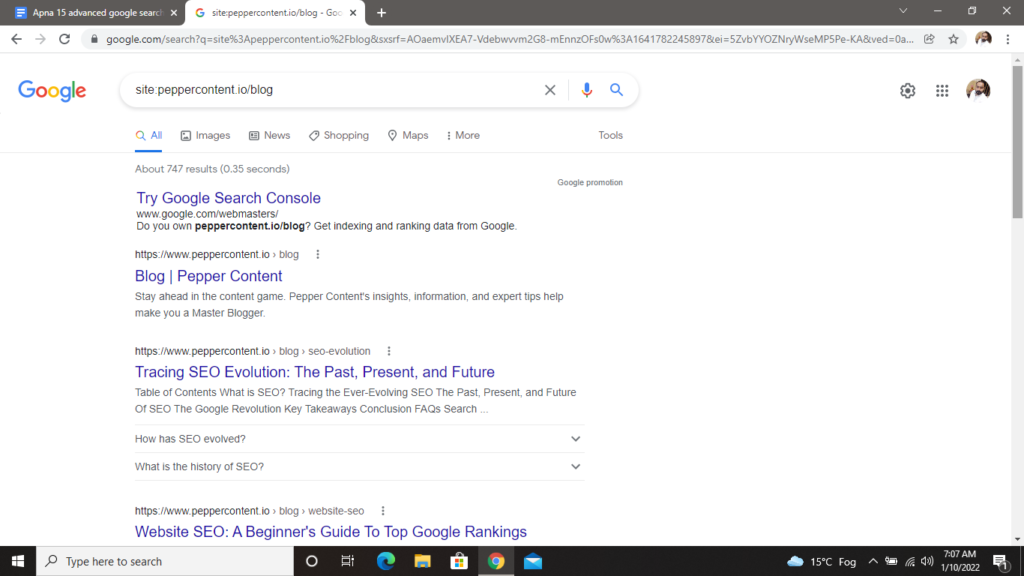
6. “intext:” command
If you begin your query with “intext:”, Google will return pages that contain the query word you provide in the search box. If your search term includes more than one word, then use “allintext:” at the beginning of your query. For instance, “allintext: content writing tips” will display only those pages in which the words “content”, “writing”, and “tips” are present.
A basic plagiarism search can also be done with the command. By taking a recognizable and distinct phrase from your content and putting it in the search box, you can find out if Google is indexing any other pages with that precise phrase.
7. “inurl” command
If you use “inurl:” in your search, Google will only show you pages that have that term in the URL. If your search term includes more than one word, then use “allinurl:” at the beginning of your query. For example, the query “inurl:healthy eating” returns documents with the phrase “healthy eating” in the URL.
This command has many uses. Let’s suppose you wish to boost your brand’s visibility on Google by locating websites that are your competitors. If SEO marketing is your niche, apply the “inurl” command like this: “inurl:SEO” or “inurl:SEO services”.
8. “intitle” command
When you initiate a search with “allintitle:” or “intitle”, Google limits the returns to pages that include all the keywords you specify in the title. You can use it to make your study more focused and efficient. It can also be used to determine your competitors. Let’s say you’re writing about blogging platforms and want to search all posts related to the subject. Use “allintitle: best blogging platforms” as your search command. Adding quotation marks to the command will help you make your search more specific.
Note: In image search, the operator “allintitle:” will return images whose names contain the terms that you specify.
9. “OR:” command
Google is adaptable. It understands that searching for a single word or phrase may not yield results. As a result, it allows you to look for multiples. Unlike a default search, where Google will include all the terms you provide, the “OR:” command instructs Google to return results for one or both search phrases.
For example, by typing “Best SEO practices for content creators OR SEO tips for content creators”, you are instructing Google to search for both the phrases. You can double-quote the search terms for more precise results. Note that the command should be capitalized.
10. “cache:” command
The way Google looks at our sites is different from what we see. Use this command if you want to see your web page through Google’s eyes. In other words, this command lets you view your web page as cached by Google. This will show you exactly what information about your website has been stored by Google. In the cached version of the page, Google will highlight terms that appear in your search query. For example: cache:peppercontent.io.
A useful feature of this command is that it displays the last time Google reviewed your website. If Google hasn’t visited your website in a long time, it could be a sign that you don’t update it frequently.
11. “filetype:” command
The ability to search for a particular file or file type is an oft-overlooked feature of Google search. If you’re looking for a specific file type, instead of combing through hundreds of pages, use the “filetype:” command to filter your results. Let’s assume you are seeking SEO-related PDFs. You can use the search bar to enter “SEO filetype:PDF”. This is primarily beneficial for scholarly purposes, but it can also be useful for corporate purposes. A few file types that you can use with this command include .swf, .gpx, .docx, .pdf, .rtf, .odt, .wap, and more.
12. “+” or “-” commands
In a Google search, using the “+” or “-” commands will add or remove a search phrase, respectively. If you’re looking for precise information on an individual, company, place, or any other entity, the “+” command can help you narrow down your search to those very units.
For example, if you search only Tom Cruise, the search results will be quite verified; however, if you are looking for information related to Scientology, then type “Tom Cruise + Scientology” to get exactly what you want.
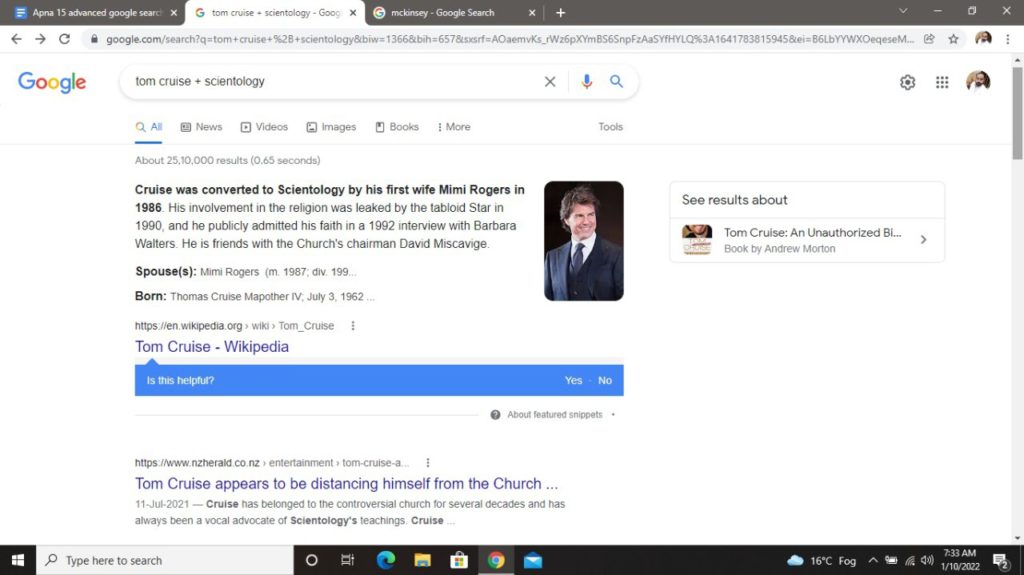
Similarly, the “-” command tells Google to search for something other than the term specified after the command. For instance, if you search William Gates -Microsoft, you would get information about William Gates, the basketball player, and not the father of Microsoft cofounder Bill Gates.
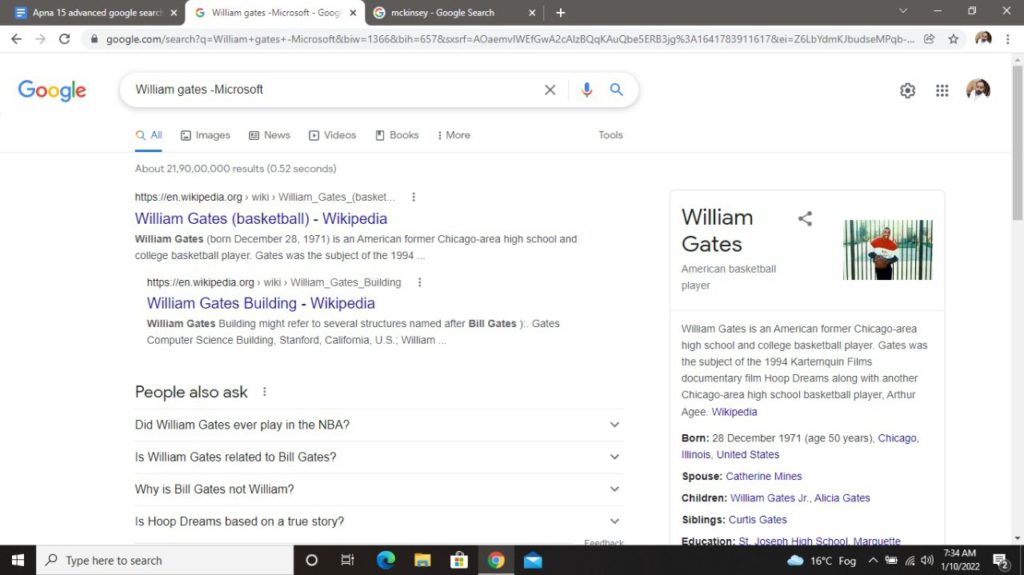
13. “location:” command
The “location:” command limits results to a single geographic location. When investigating how specific topics appear in a region or which local search phrases are popular, try using this command.
For instance, let’s assume you are writing an article about the best SUVs in the Australian market, but you reside in another country. By using the “location:” command, you can find relevant content in the search results.
14. “define:” command
If you begin your search with the “define:” command, Google will return definitions for the term from different sites. This sophisticated search operator is handy for looking up word, acronym, and phrase definitions. “define: SEO”, for example, will display definitions of SEO.
15. “related:” command
This is a powerful and unique trick that helps you discover sites and pages with identical keywords. For instance, if you are looking for a website builder other than WordPress, you can use “related: wordpress.com”. In this manner, you’ll find links to Tumblr, Squarespace, Blogger, and other blog and website builders.

Key Takeaways
- Using advanced Google search tips can prove to be immensely beneficial. These commands narrow down the searches and drill deeper into the results, giving you specifically what’s relevant to you. This makes your job easier, smoother, and more effective.
- Using commands such as intext, initle, and inurl will limit the search returns to those including the keywords you specify.
- Using quotation marks and asterisk will help you find an exact phrase or a quote. An asterisk can also be used to find lyrics of a song; meanwhile, inverted commas can be leveraged to receive specific search results.
- “+” and “-” operators will allow you to include or exclude a specific parameter from a search query. On the other hand, you can use the “OR” operator to execute multiple search queries at once.
- Use the “related:” command to find alternatives to a website. Meanwhile, when you require data from a specific website only, use the command “site:”.
- The best exercise would be to practice these Google search tips consistently and witness the impact over time. You can also combine several commands to use them in a more powerful manner.
Conclusion
According to HubSpot, Google handles around 63,000 search requests every second, for a total of 5.6 billion searches each day. Therefore, it won’t be wrong to say that Google has become an integral part of our day-to-day lives. Most of us perform multiple searches on Google on a daily basis, and know how to search on Google in a basic manner. But if you learn the advanced Google search tips and tricks mentioned above, then what seems to be an extremely simple activity can be turned into a powerful method for extracting precise information, quickly and effectively.
The best exercise would be to practice these Google search tips consistently. Moreover, though these tips are helpful for each and everyone, these would prove to be incredibly useful if you are a digital creator, who constantly needs to scan the internet for unique and reliable content.
FAQs
On your computer, do a search on google.com. Below the search box, select the type of results: All, Images, Videos, or Books. For more search options, to the right side of the search bar, click on Settings and then Advanced Search.
Some of the most popular advanced Google search tips and tricks include “site:” command, quotation marks, “OR” command, “inurl:” or “allinurl:” command, conversions, calculation, “intext: or allintext:” command, “intitle:” or “allintitle:” command, “cache:” command, “filetype:” command, “location:” command, “link:” command, and “related:” command.
Some of the popular Google search hacks include “do a barrel roll” (without the quotation marks), Google askew, Google gravity, and so on.
The most effective method to get better Google searches is to use advanced Google search tips and commands, and combine them for more precise results.
Use advanced search techniques to find more relevant and specific content. Moreover, make sure to cover all the basics, such as increasing the number of keywords in your query, removing irrelevant words, and using words that websites mostly uses.
To find an image, go to Google and choose the Images option below the search box. Type in the keywords you need an image for and hit Enter
Latest Blogs
Learn how to rank on AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini by optimizing your content for authority, structure, and relevance. Stay ahead in AI-driven search with this strategic guide.
Explore the best healthcare SEO services for your medical practice. Improve online visibility and effectively reach more patients in need of your services.
Discover top social media agencies specializing in banking solutions, enhancing financial services and driving engagement.
Get your hands on the latest news!
Similar Posts

Artificial Intelligence
6 mins read
The Role of AI in Digital Marketing: AI Article Generators Transforming Content Creation
Artificial Intelligence
4 mins read
How AI Content Creator Is Shaping the Future of Digital Content

Digital Marketing
3 mins read