5 Key Differences Between Localization and Translation

Table of Contents
- What Is Translation?
- What Is Localization?
- 5 Key Differences Between Localization and Translation
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Ask a layperson about the difference between localization and translation, and you may not receive many insights. In fact, for most, these terms are interchangeable. However, that is far from the truth. With digitization, businesses, too, are keen to cross borders. For them, the first and fundamental decision would be to choose between localization and translation.
It is easy to confuse the two. After all, both these processes involve modifying a message to enhance the experience of the audience. However, ask the practitioners in the language servicing industry, and you will know how critical it is to make the right choice when it comes to the localization vs. translation debate.
So, what is the difference between translation and localization? In order to understand this, let us first understand each’s a definition.
What Is Translation?
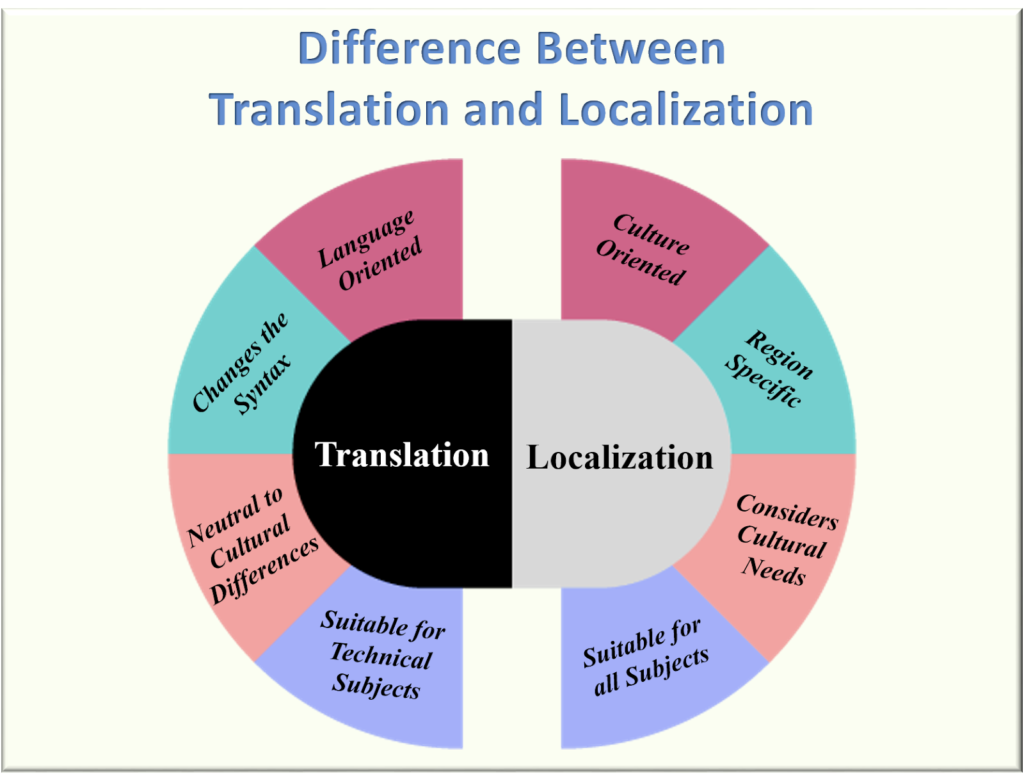
The translation is the process of changing text from an original language to a target language. With translation, you will be able to retain the core meaning of the words. However, they get expressed in a different language.

The translation is used primarily for user and training manuals, scientific and technical publications, and more. The content is simply converted without major compromises being made on syntax and other grammatical guidelines.
What Is Localization?
The process of making the entire content match the local characteristics of a language is called localization. Localization takes into account the spellings, vocabulary, cultural references, local currencies, idioms, and values while translating content.
Besides the difference between translation and localization, another buzzword doing the rounds is the industry transcreation. Transcreation helps a brand to take localization a step further by also adapting to phrases, tone, speech, and context.
5 Key Differences Between Localization and Translation
Consider these five parameters while deciding between localization vs. translation.
1. Localization starts with translation
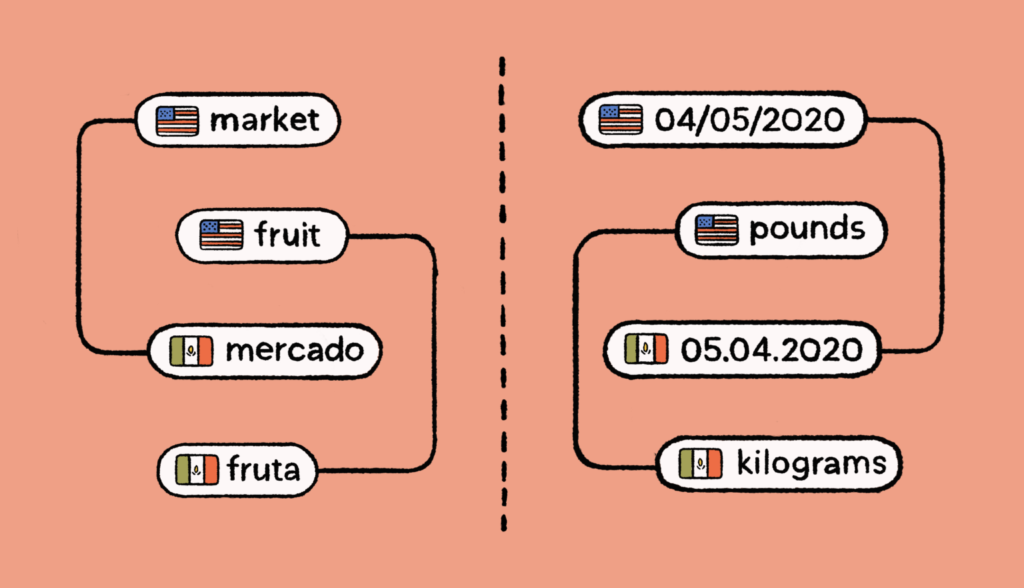
When localizing any digital or other assets for a market with a different language, the first step involved is usually translation. However, just translating your content would seldom help you connect with your audience in a new market. In order to connect with and engage newer audiences, you will need to depend on localization.
2. Localization conveys emotions
Take up a user manual about a new television set or any other electronic product, and you will find “how to use” instructions in multiple languages. You hardly require any emotion there. This makes translation an ideal choice for user manuals and all other technical subjects.
When it comes to conveying emotion, however, localization helps communicate it powerfully. Localization takes into account, not just the text used to communicate, but also the way the words are used to suit the emotions of the audience of a particular place.
3. Localization is more than just words

Localization involves not just written words, but also the images, format, layout, and more. Therefore, it is more than just translating the text into the target language. Who doesn’t know about the global sports brand Nike? Even more popular is the Nike tagline, “Just do It.” Through the use of localization strategies, Nike favorably optimizes this tagline to the audience it targets in different countries.
4. Localization encompasses cultural nuances
Localization specialists are not dependent on direct translation alone. Instead, they also take into account many culturally sensitive terms when curating content for a particular region. For example, the distance between two places is measured in miles in the United States. When the same content is translated for the Indian audience, “miles” will be converted into “kilometers.” Plus, translation can even be achieved through tools, while it may be difficult to do in localization, as the latter is more nuanced and complex.
5. Localization enhances translations
One of the easiest ways to communicate your message to a global audience would be simply to translate the content from one language to another. While this is a great first step, in all likelihood, the website would lack any real connection with the audience. The results would be completely different when the same website is modified according to the region using localization. Localization helps bridge the gap between the content and the cultural needs of the audience.
In short, in translation, you only translate the words. In localization, you translate the experience too.

Conclusion
In today’s digital age, where the consumer is spoiled for choices with respect to digital content, it is vital for businesses to deliver a high-quality user experience. Knowing the difference between localization and translation—and carefully choosing the right option based on your needs—will help you get there.
FAQs
Localization is the technique to adapt to the language, culture, and practices of the locals. Internationalization is more focused on software development, keeping in mind future markets and languages.
Interpretation is dealing with spoken language in real-time, while translation is dealing with written text or document.
Localization helps you enter new markets, gives you a competitive edge, increases customer satisfaction, and boosts brand loyalty.
The two major categories of localization are website localization and software localization.
When hiring a translator provider, you need to ensure they have good communication skills, cultural knowledge, and ample experience in the field.
Latest Blogs
Learn how to rank on AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini by optimizing your content for authority, structure, and relevance. Stay ahead in AI-driven search with this strategic guide.
Explore the best healthcare SEO services for your medical practice. Improve online visibility and effectively reach more patients in need of your services.
Discover top social media agencies specializing in banking solutions, enhancing financial services and driving engagement.
Get your hands on the latest news!
Similar Posts

Translation
5 mins read
All You Need to Know About Language Translation and Terminology Management

Translation
5 mins read
6 Reasons to Translate Content into German

Translation
5 mins read