
Table of Contents
- What are Localization and Translation?
- Localization vs. Translation with Examples
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Landing on a website that wasn’t intended for you is like traveling to a country that you didn’t plan to visit at all. You don’t know the language, currency, or exchange rate. You find it difficult to read signs, and you feel completely lost.
If you’ve ever been in a situation like this, you already understand the importance of localization and translation, although you may not exactly know what it means. People working in translation and localization services use a lot of abbreviations and jargon like – Localization =l10n. But when you talk to people from outside the industry, you’ll often notice that localization is understood as translation.
Here’s a quick overview of the meaning of localization translation and the difference between them.
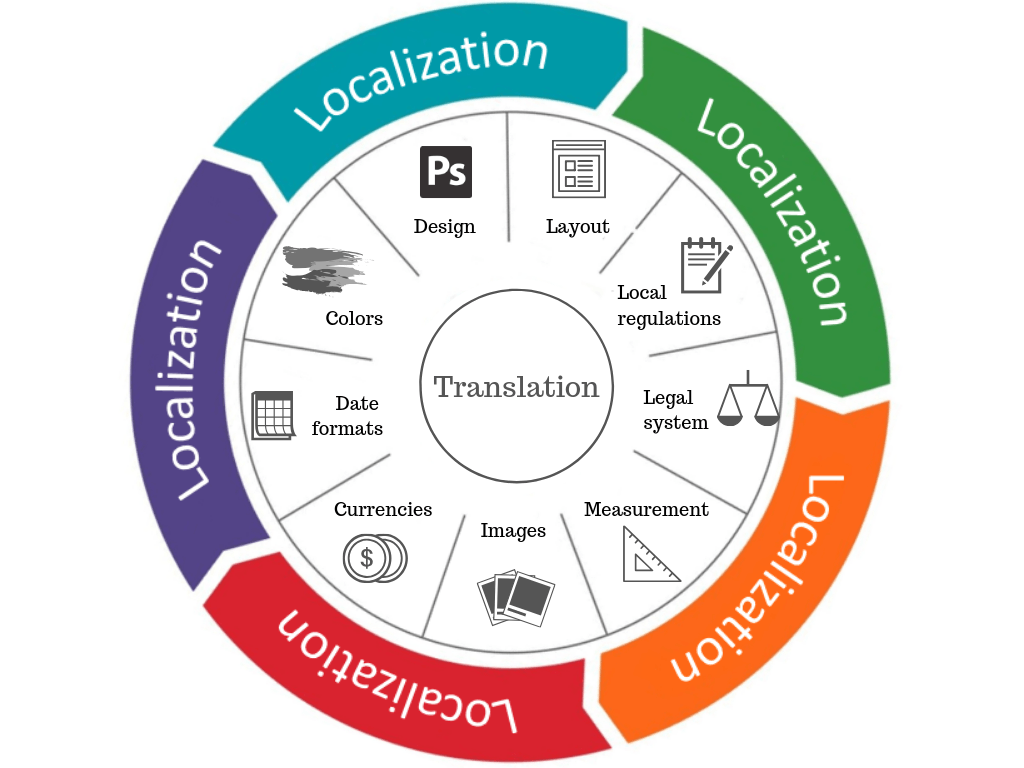
What are Localization and Translation?
Localization is the process that addresses non-textual and cultural components, including linguistic problems when adapting a service or product for another locale or country. The translation is the process of converting or rendering text from one language to another. Translation is used so that text can be understood easily. It is just one part of localization, but localization is much more extensive.
Localization involves adapting other elements as well to your target market. This includes:
- Modifying design and graphics so that it displays translated text properly.
- Converting units of measurement and local currencies.
- Changing content so that it suits preferences
- Use correct formatting for some aspects like addresses, phone numbers, and dates.
- Addressing legal requirements and local regulations.
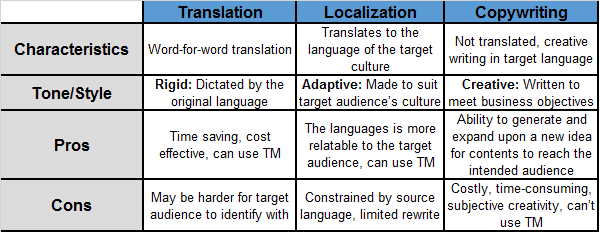
So, when you use translation, you adapt a message, while with localization, you adapt an experience.

Localization vs. Translation with Examples
Still, confused about localization and translation? Here are some quick examples to understand the difference between the two.
Translation: Apple to Las Manzanas, meaning ‘Apples’ in Spanish.
English: What is your name?
Spanish:
¿Como
se llama?
The meaning stays the same, but how it’s expressed in each language is different.
Localization: British Apple Crumble to American Apple Pie
Or
Localization translation to Localisation translation
Now, consider British English and American English – both are the same language – English. So, you do not need to translate it, but you do need to localize it. When it comes to localization, the language is the same, but if you are trying to localize it from British English to American English, then you will notice the following:
- Spellings may be different. So, s’s become z’s and ou’s become o’. For example, localise becomes localize and colour becomes color.
- Certain words may also be used differently.
- Idioms and expressions are different.
- Visuals may also need to be looked at because cultures are also different.
Localization is much more than translation. It includes translation and addresses other elements and factors such as local idioms, text length, measurement units, cultural references, page sizes, and date formats.

Key Takeaways
- People working in translation and localization services use a lot of abbreviations and jargon. But when you talk to people from outside the industry, you’ll often notice that localization is understood as translation.
- Localization is the process that addresses non-textual and cultural components, including linguistic problems when adapting a service or product for another locale or country.
- Translation is the process of converting or rendering text from one language to another. Translation is used so that text can be understood easily. It is just one part of localization, but localization is much more extensive.
Conclusion
To summarize, translation converts or transforms text, while localization transforms the entire content or product from one language to another. You can find plenty of e-learning translation services online to help you with localization and translation for your business.
FAQs
Translation is not enough to connect with your audience; hence localization is important when you don’t need to translate text but are looking to cater to cultural differences.
A localization strategy is how a brand or business adapts its message to a particular culture or language.
The main localization elements include layout, multimedia, text, fonts, character sets, and locale data.
Localization of a product means modifying or adapting a service or a product for a specific region, culture, or language.
Latest Blogs
Learn how to rank on AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini by optimizing your content for authority, structure, and relevance. Stay ahead in AI-driven search with this strategic guide.
Explore the best healthcare SEO services for your medical practice. Improve online visibility and effectively reach more patients in need of your services.
Discover top social media agencies specializing in banking solutions, enhancing financial services and driving engagement.
Get your hands on the latest news!
Similar Posts

Translation
5 mins read
All You Need to Know About Language Translation and Terminology Management

Translation
5 mins read
6 Reasons to Translate Content into German

Translation
5 mins read