
Table of Contents
- What is SERP?
- Features of SERP
- SERP Tools
- A Quick Primer on Google’s SERP
It’s difficult to talk about SEO without mentioning the Google SERPs or search engine results pages. When a user looks at a Google SERP, they are looking for information. On the other hand, a digital marketer sees hurdles and potential in a SERP. Every content marketer expects to win their SEO battles on Google’s SERPs. Let’s learn more about what SERP is and its benefits.
What is an SERP?
The acronym SERP stands for search engine results page. An SERP is a web page catalog that appears when Google searches about anything. Because Internet search engines are personalized for each individual, each SERP is unique, even for identical search phrases.
An SERP typically includes organic and paid results, but it has recently expanded to incorporate bits, images, video snippets, and location-specific outcomes.

Features of SERPs
Any result on a Google SERP that isn’t organic is referred to as an SERP feature or component.
The following are the most prominent SERP features:
- Rich snippets
A rich snippet includes more information than a regular snippet, such as images, reviews, and customer ratings. A rich snippet is any organic search result that contains more information beyond the page title, URL, and meta description.
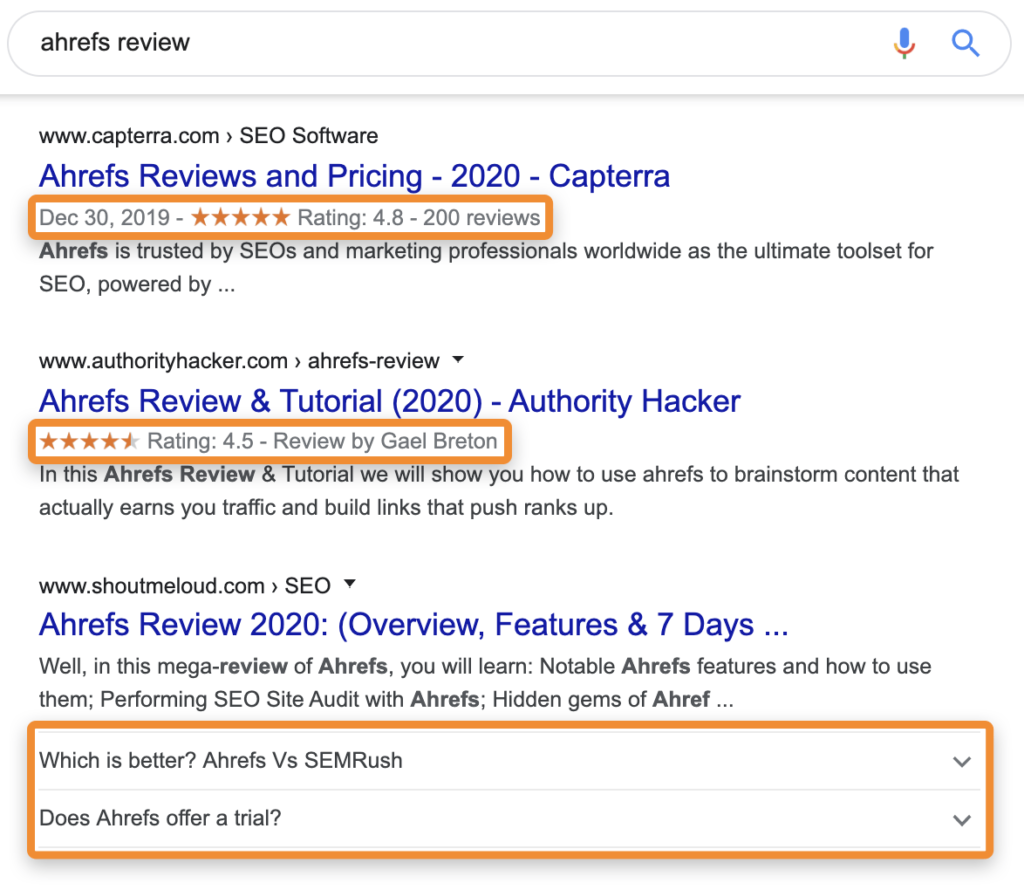
Site owners can use structured data markup in their HTML to assist search engines in comprehending and optimizing their websites for rich snippets.
- Paid results
The adverts and sponsored posts at the top of the SERP are known as paid results. Google distinguishes paid from organic results by labeling them as sponsored or ad, as shown below, or by boxing them off in a separate section of the page or using another visual indication.
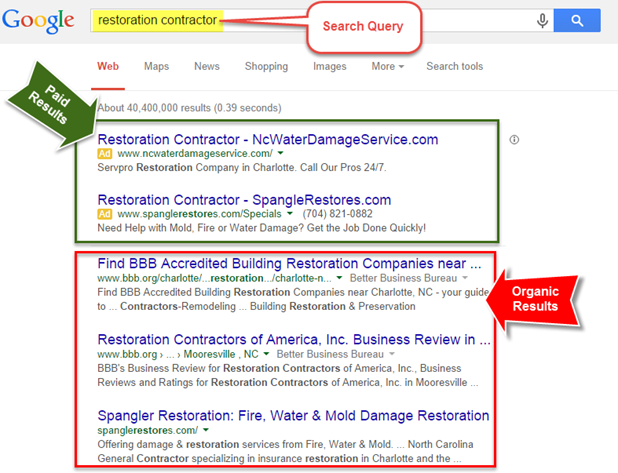
- Local SERP
Local SERPs will appear when your search intent is implicitly related to location. If you type “movie halls,” “shopping malls,” or the name of a specific product sold in stores, for example, Google will surface nearby locations that correspond to your query and show you precisely where you can find them on a map.
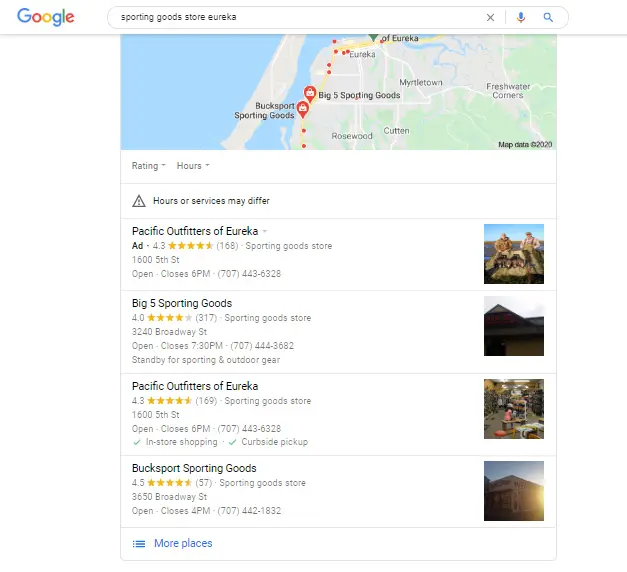
- Knowledge graph data
When your question is likely to have only one response — for example, “what is the temperature?” or “who is married to Shahrukh Khan?” — Google will display a knowledge graph, which is a box that pulls the answer to your query directly from an organic result and displays it at the top of the page.
- Universal results
Google’s strategy of combining results from its other vertical columns, such as Google Images and Google News, into the search results is known as universal results.
Google’s accentuated snippets, which answer in a box at the crown of the page so patrons don’t have to go into any organic results, are an excellent example of universal results. Other examples include images and news results.
- Vertical search
When your search needs Google to draw data from other categories, such as photographs, news, or video, a vertical search box is displayed at the top of the page. Vertical search is typically associated with subjective investigations such as geographic locations; for example, when you search “Delhi, India,” Google returns a “Things to do in Delhi” along with a “Delhi in the News” box.

SERP Tools
Now that you’ve learned about the various SERP components and what SERP is, you’re undoubtedly asking how you might improve your SERP ranking and how you’ll be able to capture a feature such as a local SERP or global results.
Here are some of our favorite tools for evaluating your current SERP position, comparing keyword rankings to competitors, and determining how to rank higher.
- WhatsMySerp: It is an avant-garde SEO tool that scans and analyses your keyword rankings and overall website rating on SERP.
- Moz Pro: A key feature of Moz Pro is that it delivers strategic guidance on ranking higher. It also crawls your site code for technical flaws, which aids search engines in comprehending your site and helping you rank higher.
- RankWatch: It analyzes your URLs, backlinks, keywords, and other SEO aspects in detail. The program also performs a comparative examination of your competitors’ websites, including the number of terms for which they rank, so you can plan how to outrank them in search results.
- SerpBook: This is a handy organizing tool for assigning groups of keywords to individual clients and scheduling the reports you should send to clients. It also allows clients to log into your account and check their ratings if you’re an SEO professional.
- SemRush: It can help you compete for SERP features like highlighted snippets, local SEO, Knowledge Graph data, and Google News by determining which keywords your competitors are ranking for.
A Quick Summary
Now you have quite an idea about what SERP is. SEO success may appear complicated and time-consuming at first, but it is well worth the effort in the end. Whatever your SEO objectives are, improve your game by streamlining your techniques by understanding the basics of SERPs and their unique features that will help you rank well on any search engine.
Key Takeaways
- Remember to keep the SERP intent in mind. Material that does not serve the SERP purpose will not rank, no matter how good it is.
- Using the SERP to your advantage will allow you to approach SEO cost-effectively for your business while also establishing your brand as an authority in your field.
- In SEO, competitor analysis is integral. If you’re having trouble grabbing the top rankings, there’s no harm in looking at what your competitors are doing.
- Optimize your content regularly to increase your chances of success. Ensure that the content is enhanced. Once the content is available, you must use all available resources to drive traffic, whether it’s through social media or an email campaign.
- Not only from an SEO standpoint, but for many users, the SERP is their first engagement with your company. We can view the user journey from beginning to end by assessing it, which forces us to see the whole picture and can help us uncover possibilities.
FAQs
Google’s answer to a user’s search query is Search Engine Results Pages (also known as ‘SERPs’ or ‘SERP’). Organic search results, sponsored Google Ads results, featured snippets, knowledge graphs, and video results are commonly found on SERPs.
Understanding SERPs and studying search results can help you understand the fundamental elements of a result listing. It also aids in determining the exact requirements for ranking a distinct keyword (s). As a result, it is a crucial component for SEO experts.
SERP positions are the positions a website holds in organic search. For example, if your website is well optimized, it will typically rank first when searching for your company’s name. The number one place begins with the top result under any paid advertisements and is counted from there.
The proportion of traffic a website obtains from its rankings in organic search results is known as search engine visibility (also known as ‘search visibility’ or ‘SEO visibility’).
This multi-faceted strategy uses SEO to ensure that the keyword takes as much space on the targeted Google SERP as possible. It also involves considering each search query as a whole.
Latest Blogs
Learn how to rank on AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini by optimizing your content for authority, structure, and relevance. Stay ahead in AI-driven search with this strategic guide.
Explore the best healthcare SEO services for your medical practice. Improve online visibility and effectively reach more patients in need of your services.
Discover top social media agencies specializing in banking solutions, enhancing financial services and driving engagement.
Get your hands on the latest news!
Similar Posts

Content Marketing
4 mins read
11 Best B2B Content Marketing Agencies for B2B Companies in 2024

Content Marketing
5 mins read
Top ecommerce Marketing Agencies with Proven Strategies for 2024

Content Marketing
5 mins read